The Model outputs tab displays text output from PlumeRise, providing data which characterizes the solution. The image below shows an example in which parameter sets 1 and 2 are active.
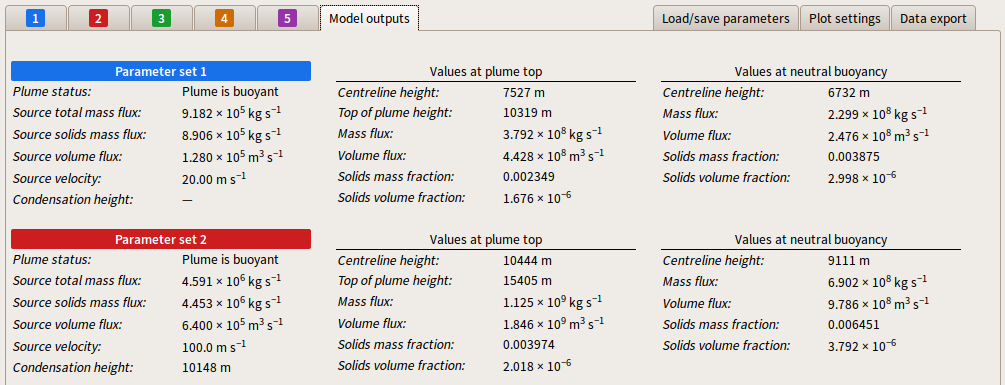
The table below gives details of the data provided in Model outputs.
| Output parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Plume status | Indicates whether the plume became buoyant or collapsed. If the mass fraction of solids at the vent is high the bulk density of the erupted material can be significantly larger than the density of the atmosphere. The material here rises due to the momentum it carries on leaving the volcanic conduit. Entrainment, heating and expansion of atmospheric air rapidly reduces the bulk density of the eruption column, and the bulk density may fall below the ambient density. However, the kinetic energy of the erupted material could be expended before sufficient entrainment has occurred to produce a buoyant plume. In this case the eruption column collapses rather than ascent high into the atmosphere. |
| Source total mass flux | The total mass flux of material at the volcanic source. The mass flux, Q, is given by 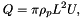
where ρp is the bulk density of the plume, L is the top-hat radius, and U is the top-hat velocity along the plume centreline. At the source, the plume radius is taken to be the vent radius, and the velocity is taken to be the exit velocity of material from the vent. The material erupted at the vent is composed of solid pyroclasts and magmatic gases (here assumed to be entirely water vapour), each of which contributes to the total mass of the plume. The density at the source is therefore a function of the gas mass fraction, solids density, temperature and pressure, 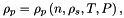
where n is the mass fraction of gas, ρs is the density of solid pyroclasts, T is the temperature of material exiting the vent, and P is the pressure (assumed equal to atmospheric pressure). |
| Source solids mass flux | The mass flux of solid material (ash) at the volcanic source. The solids mass flux, Qs, is given by 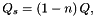
where n is the mass fraction of gas and Q is the total mass flux. |
| Source volume flux | The total volume flux at the volcanic source.
The total volume flux, V, is given by 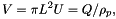
where L is the top-hat radius of the plume, and U is the top-hat velocity along the plume centreline, Q is the total mass flux, and ρp is the bulk density of the plume. At the source, the plume radius is taken to be the vent radius, and the velocity is taken to be the exit velocity of material from the vent. |
| Source velocity | The vertical component of the top-hat velocity of the material at the source. If 'Specify source velocity' is selected in the 'Parameters' tab, this reproduces the specified source velocity. If 'Infer source flux from observed plume rise height' is selected in the 'Parameters' tab, the source velocity which is determined by the inverse solver is displayed. |
| Condensation height | The height above sea level at which water vapour in the plume begins to condense to liquid water. If the plume does not reach the height at which condensation in the plume occurs, no value is returned. |
| Values at plume top | The following set of output parameters correspond to values at the plume top height, where the vertical velocity of the plume vanishes. |
| Centreline height | The height above sea level of the plume centreline at the plume top. |
| Top of plume height | The height above sea level of upper edge of the plume.
The height of the upper edge of the plume, Hu, is given by 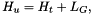
where Ht is the plume centreline height at the plume top, and LG is the Gaussian plume width. |
| Mass flux | The total mass flux of the plume at the plume top height.
The mass flux, Q, is given by 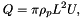
where ρp is the bulk density of the plume, L is the top-hat radius, and U is the top-hat velocity along the plume centreline. |
| Volume flux | The total volume flux of the plume at the plume top height. The total volume flux, V, is given by 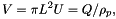
where L is the top-hat radius of the plume, and U is the top-hat velocity along the plume centreline, Q is the total mass flux, and ρp is the bulk density of the plume. |
| Solids mass fraction | The mass fraction of solids in the plume at the plume top height. |
| Solids volume fraction | The volume fraction of solids in the plume at the plume top height. |
| Values at neutral buoyancy | The following set of output parameters correspond to values at the neutral buoyancy height, where the density of the buoyant plume matches the ambient atmospheric density. If the plume collapses then it does not become buoyant so values at the neutral buoyancy height are not returned. |
| Centreline height | The height above sea level at which the plume is neutrally buoyant (i.e. the density of the plume matches the density of the atmosphere). |
| Mass flux | The total mass flux of the plume at the neutral buoyancy height. The mass flux, Q, is given by 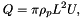
where ρp is the bulk density of the plume, L is the top-hat radius, and U is the top-hat velocity along the plume centreline. |
| Volume flux | The total volume flux of the plume at the neutral buoyancy height. The total volume flux, V, is given by 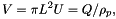
where L is the top-hat radius of the plume, and U is the top-hat velocity along the plume centreline, Q is the total mass flux, and ρp is the bulk density of the plume. |
| Solids mass fraction | The mass fraction of solids in the plume at the neutral buoyancy height. |
| Solids volume fraction | The volume fraction of solids in the plume at the neutral buoyancy height. |