The Parameters tab is used for setting source parameters for PlumeRise and the value of the entrainment coefficients. In addition, the choice of using PlumeRise in the 'forward modelling' or 'inverse modelling' modes is selected in the parameters tab. Entries are required in parameter set 1 whereas entries in parameter sets 2 through 5 inherit values from set 1.
Default parameter values can be recovered in parameter set 1 by pressing the button marked

whereas values in parameter sets 2 through 5 can be cleared by pressing the button marked
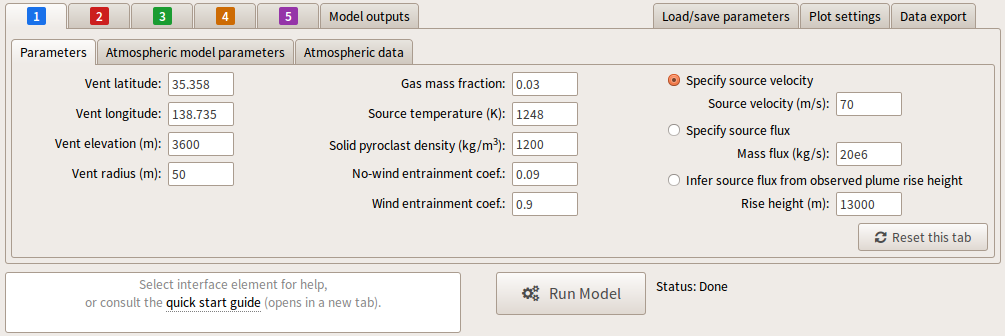
There are three selectable input parameters in the right-hand column of the Parameters tab: 'Specify source velocity', 'Specify source flux' and 'Infer source flux from observed plume rise height'. One of these options must be selected and a numerical value added to the corresponding input box.

Selecting 'Specify source velocity' allows the source velocity to be input directly.
The 'Specify source flux' option allows the source mass flux to be input. The source velocity required to obtain the requested source mass flux is then determined during the PlumeRise calculation.
The 'Infer source flux from observed plume rise height' option performs an calculation to determine the source mass flux required to obtain a specified plume height (further details of this option are available).
The table below gives a description of the parameters with typical values, the range of allowed values and shows whether a value is required. Note the range is intentionally much larger than the range of expected values.
| Parameter name | Description | Allowed values | Required? |
|---|---|---|---|
| Vent latitude: | Latitude of the plume source, in decimal form (e.g. 57.3523). | −90 – 90 | No |
| Vent longitude: | Longitude of the plume source, in decimal form (e.g. -12.0352). | −360 – 360 | No |
| Vent elevation (m): | Altitude of the plume source, in meters. | 0 – 10000 | Yes |
| Vent radius (m): | Radius of the plume source, in meters. This is the radius of the plume when the plume pressure has equilibrated with atmospheric pressure. |
0 – 5000 | Yes |
| Gas mass fraction: | Mass fraction of gas in the plume at the vent. For ash-rich eruptions the mass fraction of gas is small (less than 0.05). For gas-rich eruptions the mass fraction of gas is close to 1. |
0 – 1 | Yes |
| Source temperature (K): | Plume temperature at the vent (in Kelvin). This is the temperature of the plume when the plume pressure has equilibrated with atmospheric pressure. For dry eruptions the plume temperature is expected to be close to the magmatic temperature. For eruptions that involve the interaction with surface water, the plume temperature could be much lower than the magmatic temperature. |
0 – 5000 | Yes |
| Solid pyroclast density (kg/m3): | The density of the solid particles erupted from the vent that are carried with the gas. Large particles the follow ballistic trajectories are neglected (while these tend to be the larger particles, they are less numerous the smaller particles and therefore account for less mass. There are wide ranging values for the solid pyroclast densities, with pumice fragments density in the range 700–1200 kg/m3, glass fragments in the range 2350–2450 kg/m3, crystals and minerals in the range 2700–3300 kg/m3, and other rock fragments in the range 2600–3200 kg/m3 (source:USGS). A typical value to represent a mixture of pyroclasts is 1200 kg/m3. |
0 – 5000 | Yes |
| No-wind entrainment coef.: | Entrainment coefficient multiplying the component parallel to the plume trajectory of the velocity difference between the plume and the ambient. The entrainment coefficient is a parameterization of the turbulent mixing of the plume with the environment, here due to the relative motion of the plume and the atmosphere. The no-wind entrainment coefficient parameterizes the mixing that would occur in the absence of a cross wind. Several laboratory experiments have found values around 0.09 for buoyant plumes. |
0 – 2 | Yes |
| Wind entrainment coef.: | Entrainment coefficient multiplying the component perpendicular to the plume trajectory of the velocity difference between the plume and the ambient. The entrainment coefficient is a parameterization of the turbulent mixing of the plume with the environment, here due to the alignment of the wind field with the local normal to the plume axis. Our plume model adopts the entrainment formulation of Hewett, Fay & Hoult (1971). Values for the wind entrainment coefficient in the range 0.5–0.9 have been suggested. |
0 – 2 | Yes |
| Source velocity (m/s): | Plume velocity at the vent. This is the vertical velocity of the plume when the plume pressure has equilibrated with atmospheric pressure. |
1 – 500 | If 'Specify source velocity' is selected |
| Mass flux (kg/s): | Source mass flux |
1 – 1011 | If 'Specify source flux' is selected |
| Rise height (m): | Observed maximum rise height of the plume. The maximum height is the altitude of the centreline at which the vertical component of the plume velocity vanishes. |
1 – 100000 | If 'Infer source flux from observed plume rise height' is selected |